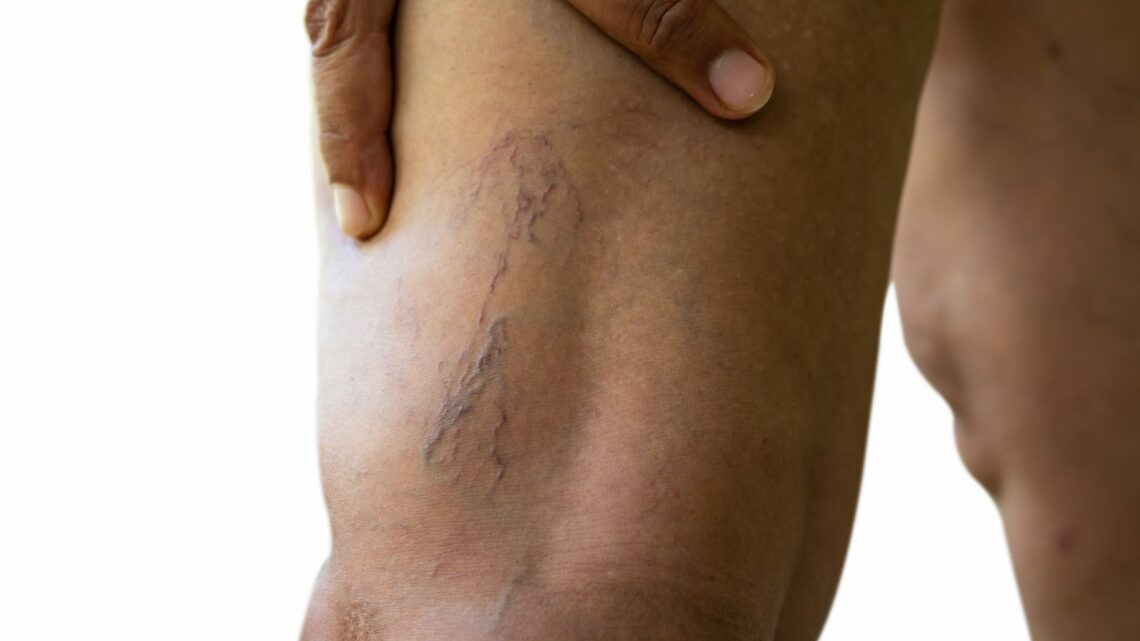
Blood clots in veins can become life-threatening if not addressed on time. A blood clot, also known as thrombosis, occurs when blood thickens and clumps together inside the veins. While clotting is necessary to stop bleeding from injuries, abnormal clotting can block veins and disrupt blood flow, increasing the risk of serious conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism.
What are Blood Clots in Veins?
A blood clot in the vein occurs when blood hardens and clumps inside the veins, instead of flowing smoothly. Clots can partially or fully block blood flow. In serious cases, a clot can travel to the lungs or heart, causing life-threatening complications like stroke or pulmonary embolism. Recognizing the symptoms early is crucial to prevent these severe outcomes.
Causes of Blood Clots in Veins
Several factors can trigger the formation of blood clots in veins. Let’s take a closer look at the common causes:
- Prolonged Immobility or Sitting for Long Periods
Sitting or lying down for an extended time—like during long flights or hospital stays—can slow blood circulation, increasing the risk of clot formation. - Injury or Surgery
Damage to the veins from surgery or an injury can cause blood to clot abnormally in that area, disrupting normal blood flow. - Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle
Excess body weight puts pressure on the veins, slowing circulation. Lack of physical activity further contributes to clotting risks. - Pregnancy and Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy can thicken blood, making clots more likely, especially in the legs. Hormonal medications like birth control pills or hormone therapy also increase the risk. - Chronic Conditions like Diabetes or High Blood Pressure
Diseases like diabetes, high blood pressure, or heart conditions damage the blood vessels, making clot formation easier. - Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Smoking damages blood vessels and reduces oxygen levels in the blood, contributing to clot formation. Similarly, excessive alcohol intake affects circulation. - Genetic Disorders
Some people inherit clotting disorders that make their blood thicker than normal, putting them at a higher risk of thrombosis.
Symptoms of Blood Clots in Veins
The symptoms of a blood clot in the veins depend on where the clot forms. Recognizing the signs early can help you take timely action.
- Swelling: The affected area, especially the legs, may swell and feel tight.
- Pain or Cramping: You may experience sharp pain, cramping, or heaviness, especially in the calf or thigh.
- Redness and Warmth: The skin around the clot may appear reddish or feel warmer than other parts.
- Shortness of Breath: If the clot travels to the lungs, you might experience difficulty breathing or chest pain.
- Fainting or Dizziness: A clot in the lungs or brain can reduce oxygen supply, causing dizziness or fainting spells.
Complications of Untreated Blood Clots
Ignoring the symptoms of blood clots can lead to severe health problems. Some common complications include:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): A clot that forms in the deep veins, usually in the legs, causing pain and swelling.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): When a clot travels to the lungs, it blocks blood flow and can become life-threatening.
- Stroke: If a clot forms in the brain or blocks blood vessels leading to it, it can cause a stroke, affecting speech and movement.
Tips for Blood Clots
Prevention is the best way to reduce the risk of blood clots forming in veins. Here are some practical tips to keep your blood flowing smoothly:
- Stay Active: Regular exercise improves circulation and lowers the risk of clot formation. Avoid sitting for long hours; take breaks to walk around every 1-2 hours.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: A balanced diet and weight management reduce pressure on your veins.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water helps keep your blood thin and reduces clotting risks.
- Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Both smoking and alcohol affect circulation and increase clotting tendencies.
- Wear Compression Stockings: If you’re prone to DVT, compression stockings can improve blood flow in your legs.
- Follow Medical Advice: If you’re on medications like blood thinners, take them as prescribed to prevent clotting.
Conclusion
Blood clots in veins are a serious health concern, but they can often be prevented with the right lifestyle changes and timely care. Recognizing the symptoms—such as swelling, pain, and redness—early on can make all the difference in avoiding severe complications. If you suspect a clot, consult a healthcare provider immediately. Stay active, eat well, and follow your doctor’s advice to keep your veins healthy and reduce the risk of blood clots.
If you have any queries related to medical health, consult Subhash Goyal or his team members on this given no +91 88008 25789, +91 99150 99575, +918283060000